Architecture Overview
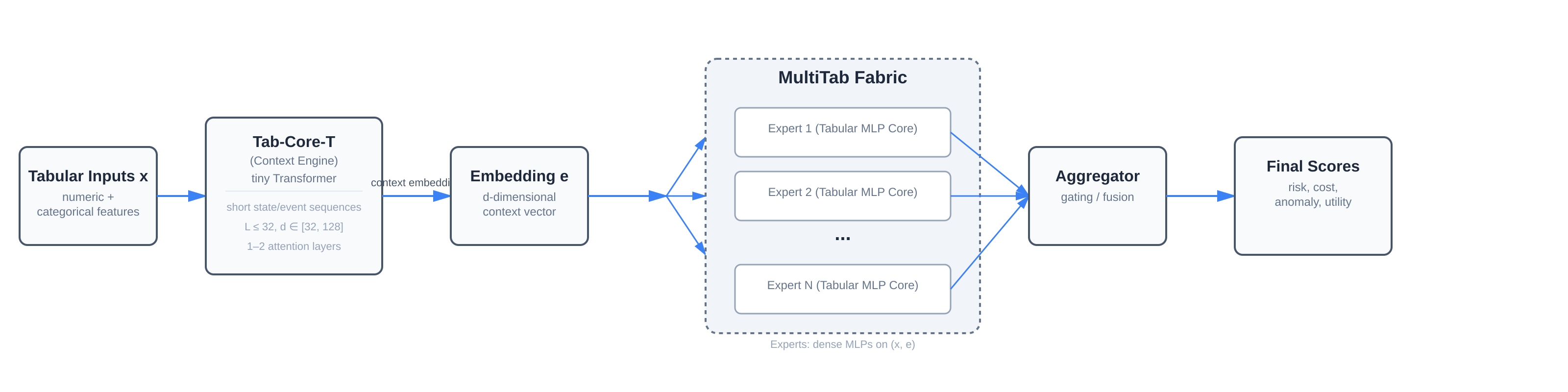
MultiTab-Core-T is a specialized ASIC architecture designed for safety-critical decision-making on planetary rovers, where power budgets (few watts), radiation tolerance, and communication delays (minutes to tens of minutes) make deploying large AI models impractical. The architecture combines two core components: (1) a tiny Transformer-based context engine that encodes short state and event histories, and (2) an array of efficient tabular MLP cores that evaluate trajectory risk, energy costs, and anomaly scores from numeric sensor features.
System Integration
Regulators
Card DRAM
Figure 2: System-level integration showing the host CPU, PCIe link, Tab-Core card with power regulators, and the ASIC containing RISC-V control, weight memory, and MLP core array
Rather than running large models on-board, we propose a teacher–student compression framework: high-capacity teacher models on Earth (LLMs, physics simulators, vision backbones) generate training targets over extensive rover scenarios; a compact on-board student ensemble approximates their decisions within the mission's operational envelope. The resulting system targets sub-millisecond latency and sub-watt power consumption.
This paper presents the architectural design, analytical performance and energy modeling (not measured silicon), and a roadmap toward aerospace-grade implementation. The same principles apply to terrestrial high-throughput decision workloads where tabular features and short context dominate—including online advertising, recommender systems, and financial risk scoring.
📄 Download Technical Paper
Full architectural study (7 pages) including detailed system design, analytical performance modeling, energy estimates, and comparisons with CPU/GPU baselines. All 20 references included in the PDF.
For academic use: LaTeX source also available
